
In this section: How to: |
On the Format tab, the Chart Types group provides buttons for each of the five most commonly-used chart types. These include Bar (default), Pie, Line, Area, and Scatter, as shown in the following image. You also have access to Lightweight Mapping using the Map button. A button labeled Other gives you access to the complete chart library of advanced charts.

Note: For more information on how to invoke the version of InfoAssist that you are using, please see Getting Started With InfoAssist.
You can run this procedure in Query Design view or Live Preview.
The chart appears on the canvas.
You can run this procedure in Query Design view or Live Preview.
The Select a chart dialog box opens. The chart types, depicted by icons, display on the left side of the dialog box.
From top to bottom, the chart type categories are Bar, Line, Area, Pie, XY Plots, 3D, Stock, Special, and HTML5.
All supported variations of the chart type appear as thumbnail images in the dialog box.
If you are not familiar with a chart type, be sure to read the description carefully before finalizing your selection. Some chart types require a certain number of data values, or a certain type of data values. If your data does not satisfy the requirements, the chart will not accurately represent the data.
In the following image, the Pie chart type is selected. To the right, the dialog box displays thumbnail images of the chart variations that are supported. Once a selection is made, a description for that chart appears underneath.

You can also hover over an image with your mouse to display the chart type name, as shown in the following image.

You can run this procedure in Query Design view or Live Preview.
The chart appears on the canvas.
The series appears in the new chart type.
When you create a dual-axis chart, you assign one data series to the Y1 axis and another data series to the Y2 axis.
The Select a chart dialog box opens.
When you create a multi-axis chart, you assign one data series to the Y1 axis and another data series to the Y2, Y3, Y4, and Y5 axes (as needed).
The Select a chart dialog box opens.
You use the Lightweight Mapping functionality to create a map in InfoAssist.
Note: You must use the HTML5 output format to access this functionality.
The Select a map dialog box opens, as shown in the following image.
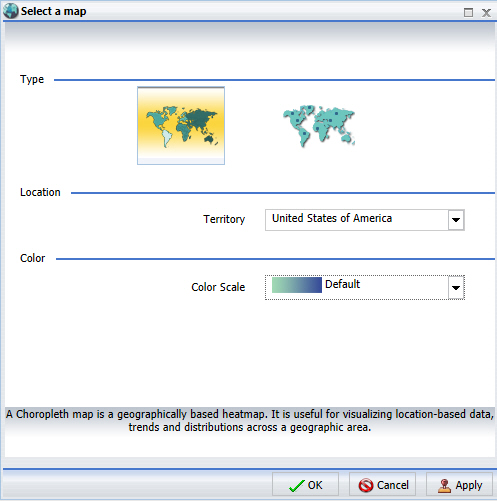
Note: This section allows you to pick geographic locations for which maps are available. You can select a territory option from the drop-down list. For example, some of the available territories include World, Europe, or United States of America.
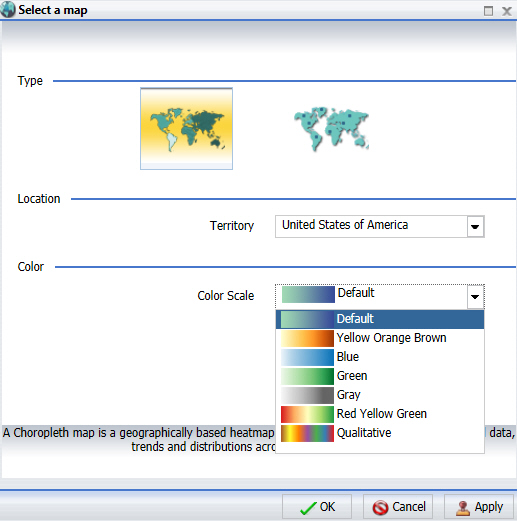
Note: This section allows you to pick a color scale for a choropleth map, as shown in the following image. For a proportional symbol (bubble) map, the color selection option is disabled.
Note: Latitude and Longitude field containers are available for proportional symbol (bubble) maps. You can specify latitudinal or longitudinal data using these fields.
When the location field is specified, the Location Type dialog box displays, as shown in the following image.
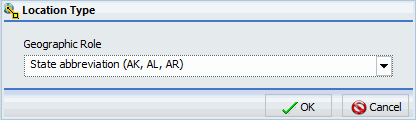
Note:
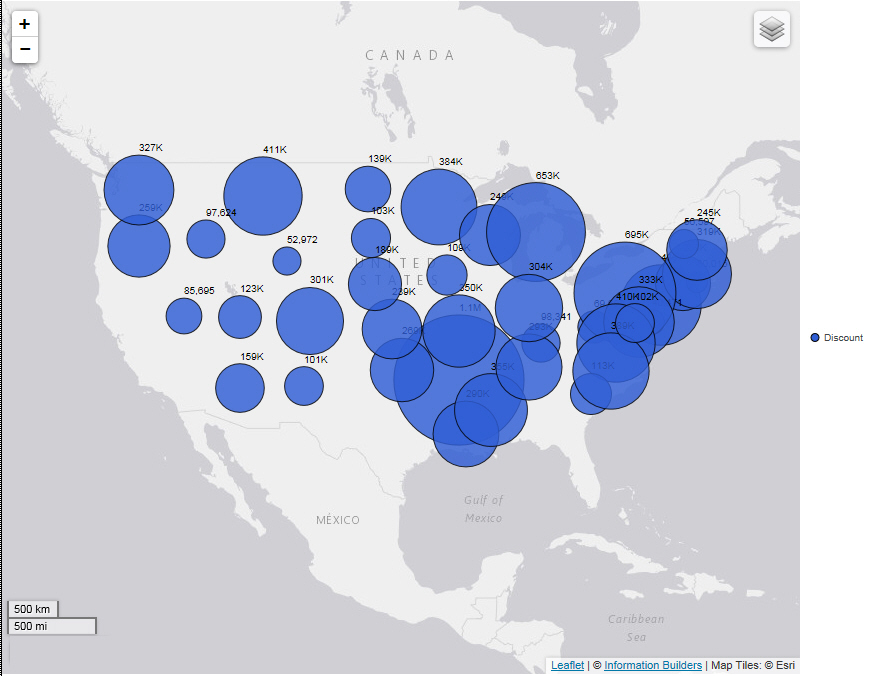
The map displays based on your data and selections for Type, Location, and Color.
For example, the following map shows the geographic location, using a proportional symbol map, of Discount data by State in the United States.
You can create charts using one of the following output formats:
The HTML5 output format allows you to render a chart in the browser using a built-in JavaScript engine. Charts with this output format utilize the very latest capabilities of the HTML5 Web standard, including animation, high-quality vector output, and attractive alpha-channel and gradient effects.
Note: Not every chart type can be output in every format listed here. To make sure that the chart that you are creating can be output in the format that you want, please see the topic for that particular chart type.
| WebFOCUS |