In this section: |
One of the strengths of WebFOCUS Visual Discovery, is the ability to select what you see on charts in projects. We call that a selection. A selection on one chart in a project is propagated to all the other charts across all the other pages in a project. This happens in simple one table projects, as well as across charts attached to multiple linked tables in a more complex project. As selections are made, underlying data can be in one of four states:




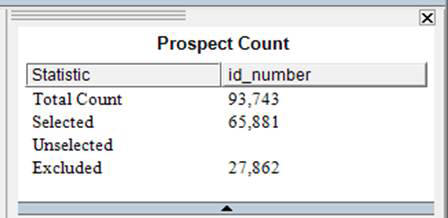
The counts chart is a great way to get a quick view of what's selected, and what's not. The first line (total count) counts all rows in the table whether included, excluded, selected, or unselected.
Note: The counts chart can also show unique counts, sums, averages, etc.) The second line shows what is selected, the third line what is included but not selected, and the fourth line shows what is excluded (both by filtering and excluding.
 . This is the default setting. The
data that you select using this tool replaces previously-selected
data.
. This is the default setting. The
data that you select using this tool replaces previously-selected
data.
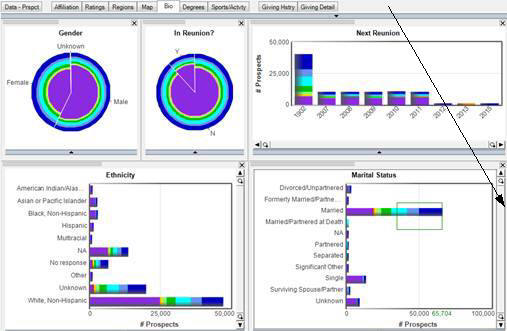
All charts on all pages update instantly based on the selection.
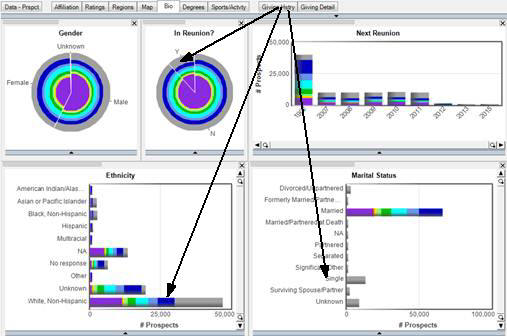
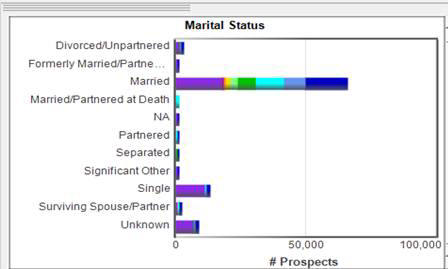
In the page above, only those individuals who are Married are now the colored portions of the bars in the Ethnicity, Gender, In Reunion, and Next Reunion charts.
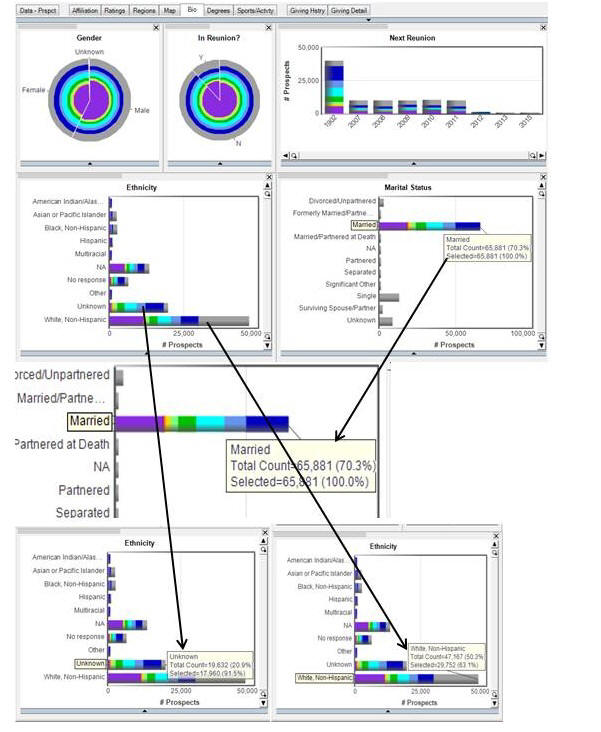
What does it mean to have selected and unselected data? When you have both selected and unselected data you are able to see the percentage of the selected data to the whole available (= non-excluded) population. In the example, below we see that 70.3% of the available population are Married, you can also see that 91.5% of the Unknown Ethnicity are Married, which is a much higher % than the larger White, Non-Hispanic group. Then you can add in unselected data, intersect with other selected data, or subtract other selected data.
 . Use this function to add data
to an existing selection. Using the Martial Status example, if you
want to add another Marital Status to the selection you have already
made, in the Add Selection Mode select another bar on the Martial
Status chart.
. Use this function to add data
to an existing selection. Using the Martial Status example, if you
want to add another Marital Status to the selection you have already
made, in the Add Selection Mode select another bar on the Martial
Status chart.
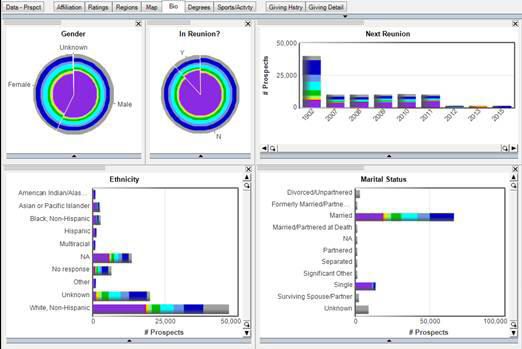
When you add more data, the other charts in the project will adjust to reflect the selection that has been made. In this case, all charts include the Married and Single population.
 . Use this function to remove data
from an existing selection. Select any bar on a chart that has already
been selected and it will subtract that selection from your entire
selection population.
. Use this function to remove data
from an existing selection. Select any bar on a chart that has already
been selected and it will subtract that selection from your entire
selection population.
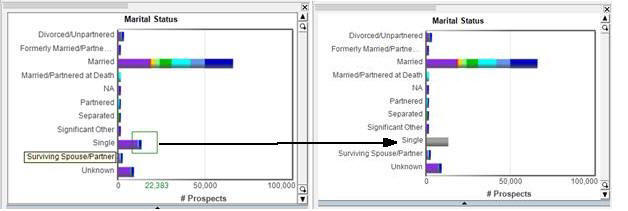
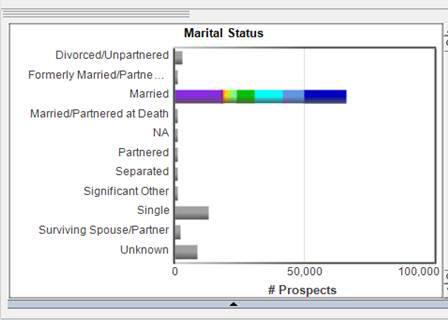
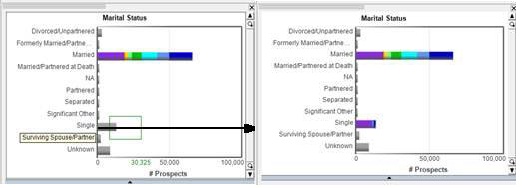
Notice in the Subtract Select Mode, when selecting the Single bar in the Marital Status chart, the Single bar goes grey as that population is now unselected.
 . Use this function to select the “intersection”
of two fields. This is essentially an “and” function. For example,
you might want to select the population that is Married and Unknown
ethnicity and Male gender.
. Use this function to select the “intersection”
of two fields. This is essentially an “and” function. For example,
you might want to select the population that is Married and Unknown
ethnicity and Male gender.
Use the top tool bar to exclude entities and then refresh the charts to show all attributes associated with the selected entities. For example, suppose you have a data set that includes geographical information, such as the State a population of individuals lives in. They may have a primary address in Illinois and a secondary or seasonal address in another state. Now let’s assume you want to exclude all those individuals that do not have an address in the state of Illinois. When you exclude from the Primary (Core) table, all those individuals that have an address outside of Illinois will be excluded. However, you will still show a population in your bar chart that includes other states. The reason for this is that all those individuals who have a Primary address in Illinois may have a secondary or seasonal address in another state and the bars for those other states remained and were not excluded. However, you will still show a population in your bar chart that includes other states. The reason for this is that all those individuals who have a Primary address in Illinois may have a secondary or seasonal address in another state and the bars for those other states remained and were not excluded. For more information, see the image below.
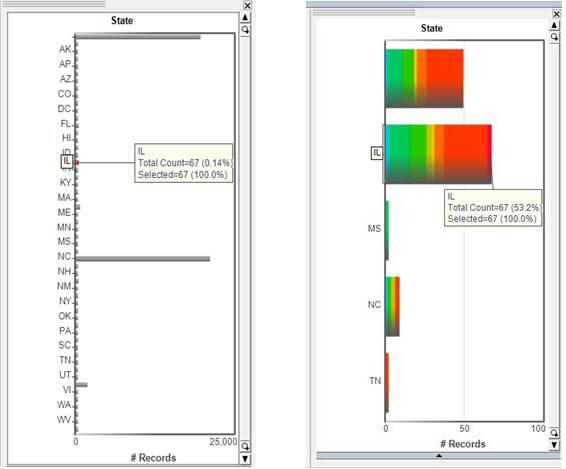
In this case there are 67 individuals living in Illinois. By excluding the unselected from the Primary or Core table by using the “Exclude Unselected” chart in the tool bar, all those individuals outside of the 67 that live in Illinois have been excluded. However, some of those remaining individuals have seasonal or secondary addresses in other states and those records were returned because they still pertain to the 67 individuals that live in Illinois. What is excluded first are individuals, and then all addresses are updated for those individuals.
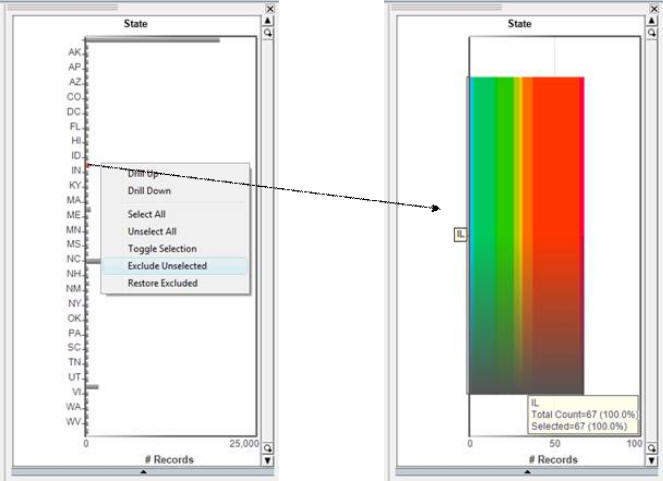
In this case because the exclusion was executed locally, all those addresses that existed outside of Illinois were excluded. This is because the exclusion occurred FIRST in the table that included the addresses, not the table that included the individuals.
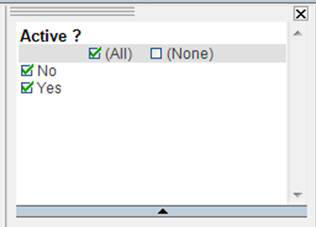
Filters are a mechanism for specifying a subset of the data from a data source that is available in an analysis session. An easy way to look at filters is as a starting point before your analysis. Suppose you have a data set of individuals and decide from the outset that you want to exclude all the males from the data set before starting your analysis. If your project has a text filter set to Gender you can remove all the males from your project by deselecting Male in the text filter box. See the following image. Notice that with both males and females selected there are 188,238 individuals represented in the data set.
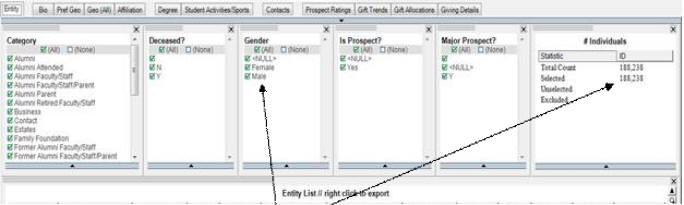
Note that when the Males are deselected from the text filter, the counts of individuals in the data set changes from 188,238 to 111,358 and the counts also show that 76,880 individuals (males) have been excluded from the data set. For more information, see the following image.
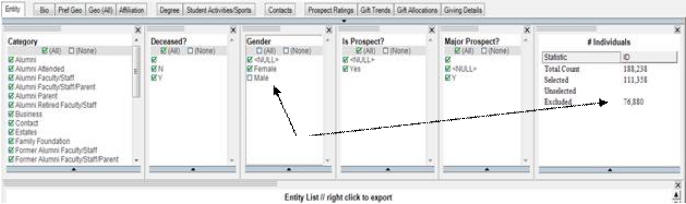
It is important to note that the only way to bring back the data that has been excluded due to a text filter is to reselect the filter and return the data to its original state. In this case, to bring back all of the males, you must reselect the Male box in the text filter.
In addition to the selection mode, you can also change the selector shape. There are three possible selector shapes:
|
Toolbar Button |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The Rectangular Selector. This is the default setting. To use the rectangular selector, place the cursor in the area to be captured and drag the mouse while holding down the left mouse button. A rectangular selection box appears around the data that you have selected. |
|
|
The Circular Selector. To use the circular selector, place the cursor in the area to be captured and drag the mouse while holding down the left mouse button. A circular selection area appears around the data that you have selected. |
|
|
The Lasso Selector. Use this tool to select data by creating freehand selection borders around the data. |
| WebFOCUS |