In this section: How to: Reference: |
Derived datapoints let you create calculations that include dimensional metadata. For example, you can create a series of derived datapoints that perform a series of calculations on Sales performance for your manufacturing company:
- Cost of Supply (by Product, Location and Time)
- Cost of Labor (by Product, Location and Time)
- Cost of Warehousing/Storage (by Product, Location and Time)
- Cost to Ship (by Product, Location and Time)
These datapoints can now be added up to become Total Cost (by Product, Location and Time).
You can then set Total Cost against your Sales (by Product, Location and Time) to calculate Profit.
You can also load precalculated Total Costs and Profit datapoints from an external Source, but there is no guarantee the data will be calculated in the proper order. If you use derived datapoints to calculate the values:
- The data will be calculated in the correct order, by using the generations in the datapoint lineage. PMF will also recognize incomplete data and handle it accordingly.
- You will be able
to deconstruct the calculations performed for all derived datapoints using
Lineage Chains.
Lineage Chains are currently available in the Lineage tabs on dimensions, sources, datapoints, and measures panels.
- Derived datapoints allow deep models of recalculation, that let many measures share the same common root calculated values.
- Derived datapoints let you mix and match any data source in one contiguous data mart, and are much easier to set up than ETL jobs. This is because dimensional aggregation logic is included in the calculations, so you do not have to write complex dimensional logic in an ETL tool.
To create a derived datapoint:
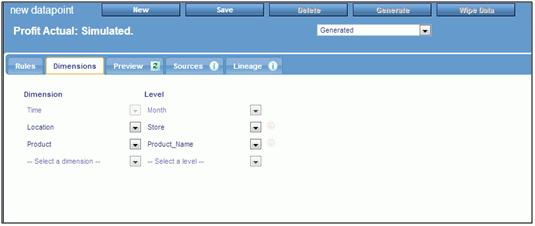
- In the Manage tab, click the Datapoints panel button.
-
Click New.
The New Datapoint panel opens.
- Name the new derived datapoint.
-
Drag the
datapoints you need for your calculation into the canvas. Each datapoint
must be separated by its operation, as shown in the following image.
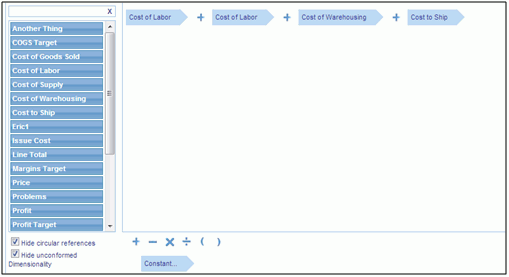
Calculations can also include constants. To add a constant, drag the Constant object into position on the canvas, and type in the constant value inside the Constant object.
Separate datapoints for WebFOCUS functions are typically created during the source load, since capturing these calculations is done best in the first-generation in the lineage, during harvesting.
For example, if you want to capture counts of a particular condition, rather than trying to save all those attributes somewhere so you can perform the filtering later, you can determine When, that is what filters should be true, for the count. You can then pull that count into a loadable datapoint. Approaching data this way allows you to make calculations in the lineage after this harvesting phase simpler for you to manage.
- Click Save. If the calculation is not complete, PMF recognizes this, and marks the derived datapoint as Incomplete. Incomplete derived datapoints do not participate in recalculation.
To change a derived datapoint:
- In the Manage tab, click the Datapoints panel button.
- Select the derived datapoint you want to change. The Edit Datapoint panel opens.
-
Make your
desired edits. You can change anything in a derived datapoint, including
the name and its formula.
Note:
- Datapoints are included in formulas and linked to measures by reference, so renaming them changes their name through the entire system.
- Altering the formula for a derived datapoint automatically flags its data, and any later generations in the lineage for that datapoint, including child derived datapoints and measure values, for a one-time wipe. If the data is also scheduled for reload, PMF performs that load after wiping the data.
You can make an exact copy of any existing derived datapoint. After making the copy, you can immediately alter it as needed. To copy a datapoint:
- From the Manage tab, click the Datapoints panel button.
- Select the derived datapoint you want to copy. The Edit Datapoint panel opens.
-
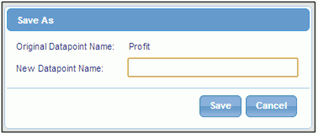
Click Save
As. You will be prompted for a new name for the derived
datapoint, as shown in the following image.
- Click Save. PMF will make an exact copy of the derived datapoint. You can edit and save your changes at any time, and click Save As again if you want to make more copies. This datapoint is what will be loaded for editing.
All loaded data from a derived datapoint can be wiped out or deleted in a single operation, because they are not attached to a source.
Note: Wiping data affects downstream datapoints for the datapoint you wipe. Every datapoint downstream is marked as having incomplete components. Incomplete components do not participate in recalculation.
- From the Manage tab, click the Datapoints panel button.
- Select the datapoint that needs to be deleted. The Edit Datapoint panel opens.
- Click the Wipe Data button. PMF will ask you to confirm the data purge.
- Click OK.
Note: It may take PMF a moment to purge all of the data.
PMF allows you to create an unlimited number of calculations for your measures using special datapoints that store and process calculations, known as derived datapoints. These calculations can be based on one or more existing datapoints, of any kind, including loadable, user-entered, generated, and other derived datapoints. Note the following:
- If you create a derived datapoint that uses data from loadable, user-entered, or generated datapoints, PMF will recalculate the results every time the data for these are changed. The data goes through the lineage, through all of your steps of calculation, until it is copied to any measures linked to your datapoints.
- If you create a derived
datapoint that uses data from another derived datapoint, PMF knows
that the “parent” derived datapoint must be calculated before calculating your
new derived datapoint. Logic built into PMF understands that calculations
must use generations in the datapoint lineage.
Recalculating a complex lineage chain through possibly hundreds of thousands or millions of row values can be an expensive operation, so you have full control over how much of this calculation is performed during normal processing hours.
Note: During scheduled load cycles, since PMF is less used during scheduled load times (usually overnight), recalculation can always go through the entire lineage.
You can preview the data that PMF will generate by clicking the Preview tab, as shown in the following image.
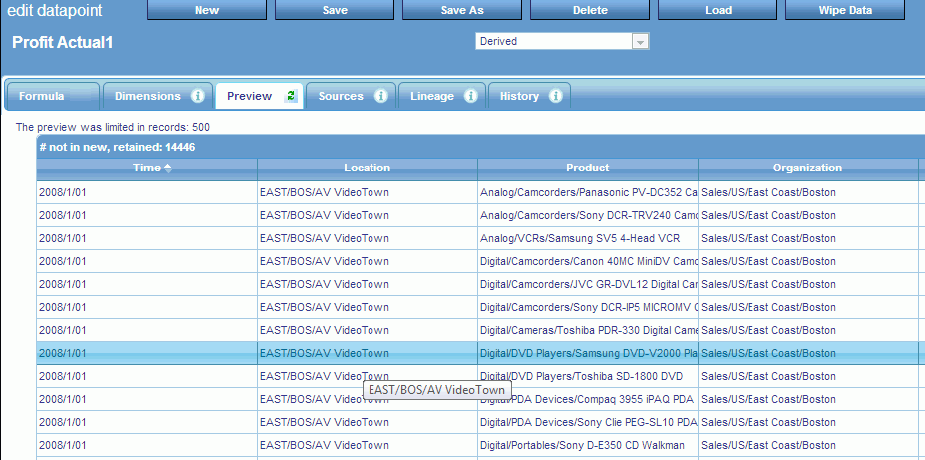
The Preview tab generally shows rows that are new, or will be updated or deleted.
Tips:
- The Preview tab shows
data to be handled before any operations occur. It divides this
data up into the following sections, based on what will happen to
the rows that are displayed:
- New rows to be created by generation.
- Rows to be updated by generation.
- Rows to be deleted by generation (depending on the Wipe Data setting on the Advanced tab).
- Rows that will be kept but whose values do not match the new data to be generated (depending on the Wipe Data setting on the Advanced tab).
- Opening the Preview tab will force the navigation bar to close, in order to use as much screen width as possible. You can reopen it by clicking the expand button at the top of the navigation bar.
- You can resort the preview contents in any order by clicking the column headings. Note that the Preview will show data based on the display limit set in the Load settings. To change this value, see Load Settings.
Derived datapoints can have a complex, multi-part lineage, depending on their relationship to other derived datapoints.
- In the lineage directionality of derived datapoints, the data in derived datapoints always progresses to the left, from first-generation datapoints (loadable, user-entered, and generated) toward measures.
- PMF automatically handles figuring out the generation of each derived datapoint in the lineage, by analyzing the first point in the lineage where a derived datapoint sends its data onward.
You can view lineage for all datapoints for any derived datapoint. Lineage shows the progress of data through PMF, from the external data harvested into datapoints, through any derived datapoints, and finally all terminal points in Measures. The Lineage tab displays the components in the generated source by default, as shown in the following image.
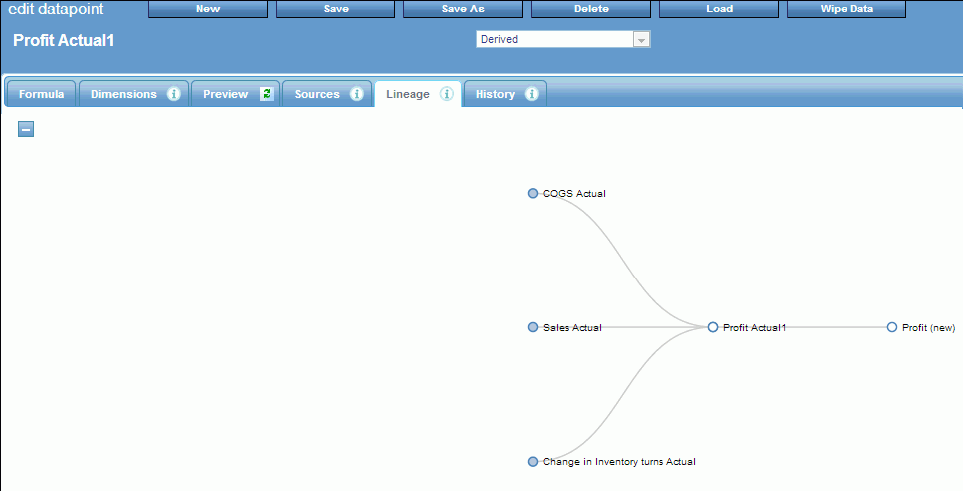
The lineage tab automatically
displays the entire lineage. You can click the Collapse
All
 button to hide the entire lineage.
button to hide the entire lineage.
PMF keeps track of each load that is executed for each derived datapoint in the system, regardless of whether you loaded it manually or the load was called by the scheduler. This data is stored in a special logging section of the PMF data mart.
The History tab on each derived datapoint displays the history of all loads that have been logged.
The history of the derived datapoint shows:
- The dates that the loads ran.
- The count of rows that were retrieved, inserted, updated, and deleted.
- The count of total mismatches that occurred between the source data and the PMF metrics mart. Mismatches are source data rows that do not match to any existing keys for one or more dimensions.
- The count of gaps in data continuity, which indicate the sparsity of the data. This does not mean there are errors but, if paired with mismatches, can help you debug any unexpected data discontinuities.
- Any messages returned from the load system. If there is an error, the exact error is displayed in the information shown in this tab.