The following procedure uses the Microsoft SQL Server pubs.dbo.authors sample table, and the Microsoft SQL Server difference scalar function, which is not available in ANSI SQL.
-
Right-click
the application directory where you want the new data flow, select New,
and then click DBMS SQL Flow.
An empty flow appears in the data flow workspace. The DBMS SQL Flow tab opens by default.
A DBMS SQL Object appears in the center of the workspace.
- Right-click the DBMS SQL object and select Properties.
- Select an adapter and connection from the drop-down menus and close the Properties panel.
-
Right-click
the SQL object and select SQL Statement.
The Select Statement dialog box opens.
-
Type
a dialect-specific SQL Statement, like the following in the Select Statement
dialog box.
SELECT au_fname, au_lname FROM pubs.dbo.authors WHERE difference (au_lname, 'delay') > 3

-
Test
your SQL by clicking the Test SQL Statement button.
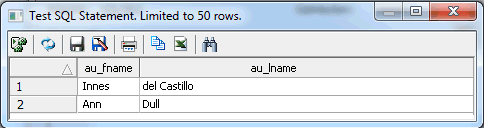
-
Click Close.
Then click OK.
Note: The SQL statement must be a SELECT statement that conforms to the dialect-specific requirements of the adapter.
-
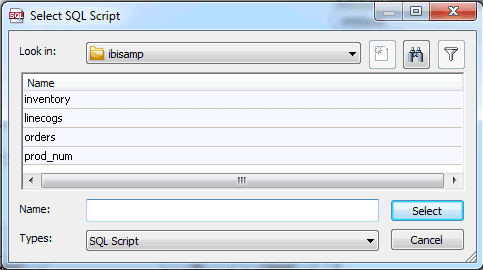
Optionally,
you can import an SQL statement from an existing .sql file by clicking
the Import button, selecting an SQL file,
and clicking the Select button. The SQL file
must be in one of your Application Directories.
-
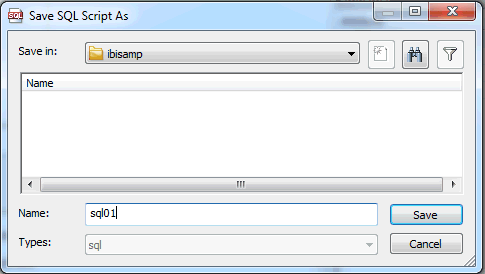
Optionally,
you can export SQL statements as .sql files for later use by clicking
the Export button. Select a Server and Application Directory
from the drop-down menus, enter a File Name, and click OK.
- Drag a data target into the workspace. You can also right-click in the workspace, select Add Target, then Existing or Add Target, and then click New.
- Click the Save button on the Quick Access Toolbar.
- Enter a name for the flow in the File Name field and click OK. You can also select a Server and Application Directory from the drop-down menus.
- Run the flow.